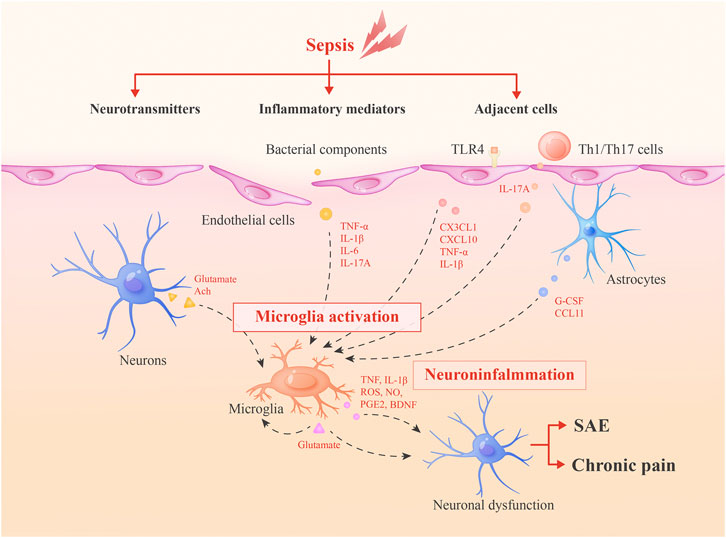
PDF) Natural Sulfurs Inhibit LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses through NF-κB Signaling in CCD-986Sk Skin Fibroblasts

Molecules | Free Full-Text | Anthocyanin-Rich Sour Cherry Extract Attenuates the Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Endothelial Inflammatory Response

The Ubiquitinated Axon: Local Control of Axon Development and Function by Ubiquitin | Journal of Neuroscience
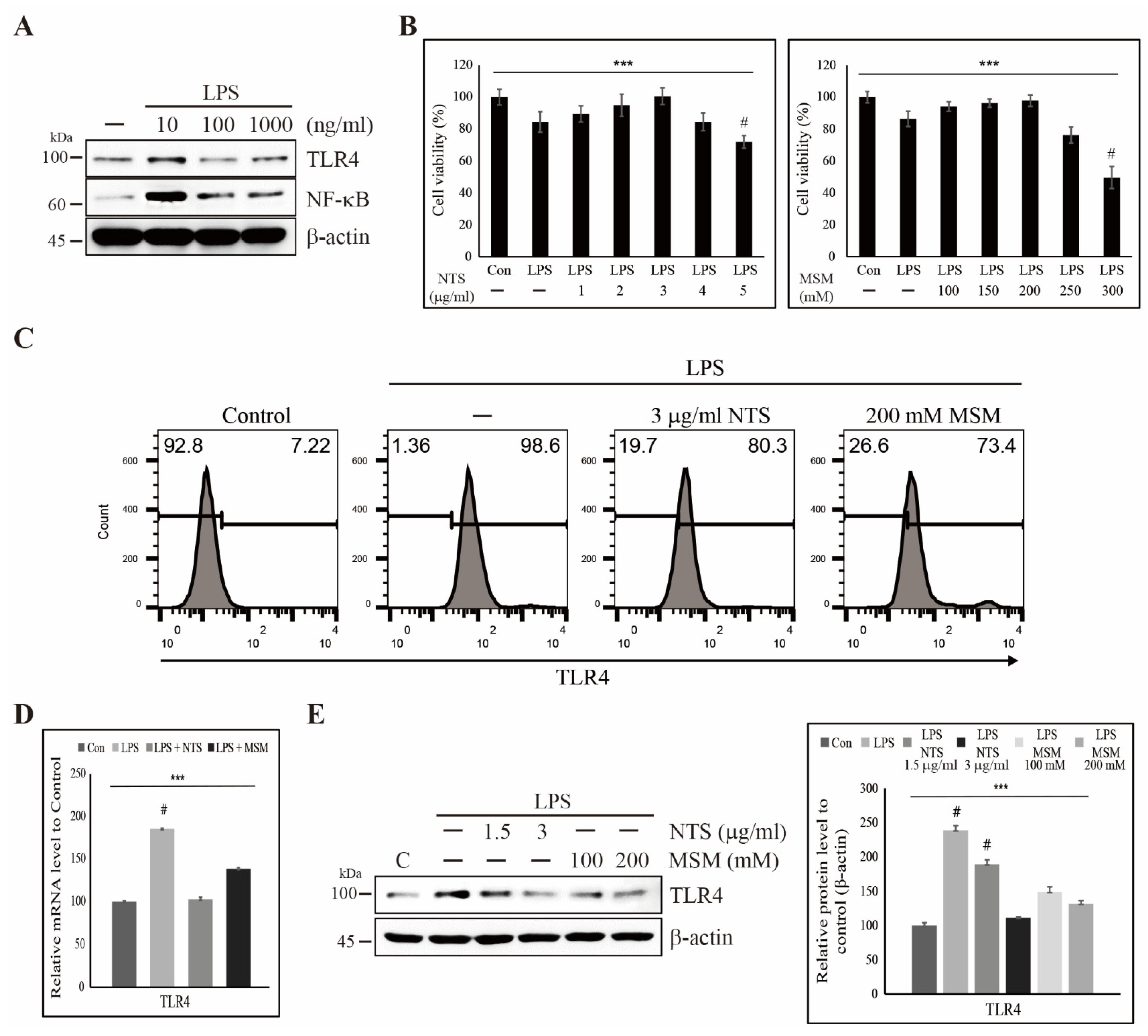
Life | Free Full-Text | Natural Sulfurs Inhibit LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses through NF-κB Signaling in CCD-986Sk Skin Fibroblasts

Computational Dissection of Membrane Transport at a Microscopic Level: Trends in Biochemical Sciences
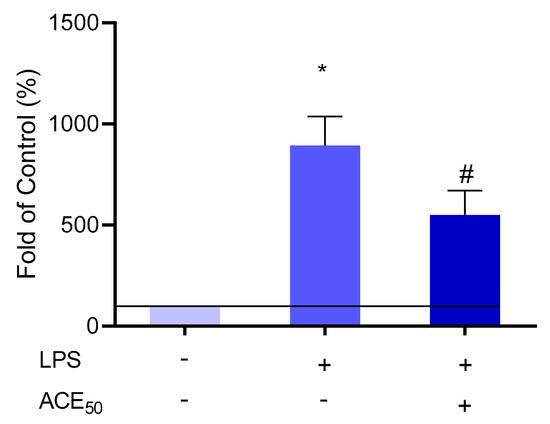
Molecules | Free Full-Text | Anthocyanin-Rich Sour Cherry Extract Attenuates the Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Endothelial Inflammatory Response

IJMS | Free Full-Text | Antibacterial Activity of Medicinal Plants and Their Constituents in the Context of Skin and Wound Infections, Considering European Legislation and Folk Medicine—A Review

CD55/decay accelerating factor is part of the lipopolysaccharide‐induced receptor complex - Heine - 2003 - European Journal of Immunology - Wiley Online Library
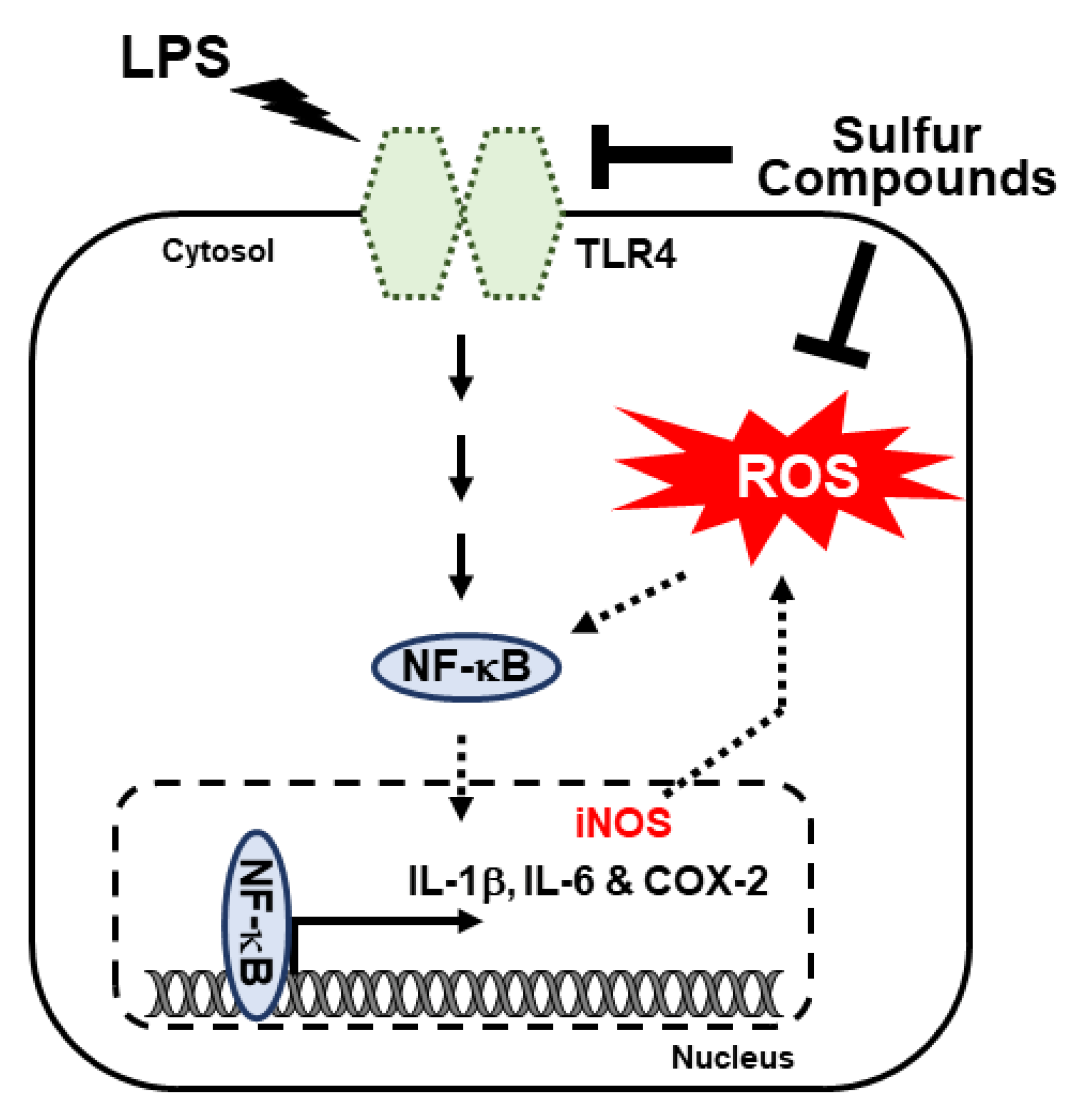
Life | Free Full-Text | Natural Sulfurs Inhibit LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses through NF-κB Signaling in CCD-986Sk Skin Fibroblasts

LPS-induced expression and release of monocyte tissue factor in patients with haemophilia | SpringerLink

PDF) Acute-Phase Concentrations of Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Binding Protein Inhibit Innate Immune Cell Activation by Different LPS Chemotypes via Different Mechanisms
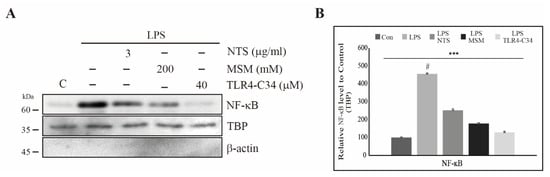
Life | Free Full-Text | Natural Sulfurs Inhibit LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses through NF-κB Signaling in CCD-986Sk Skin Fibroblasts
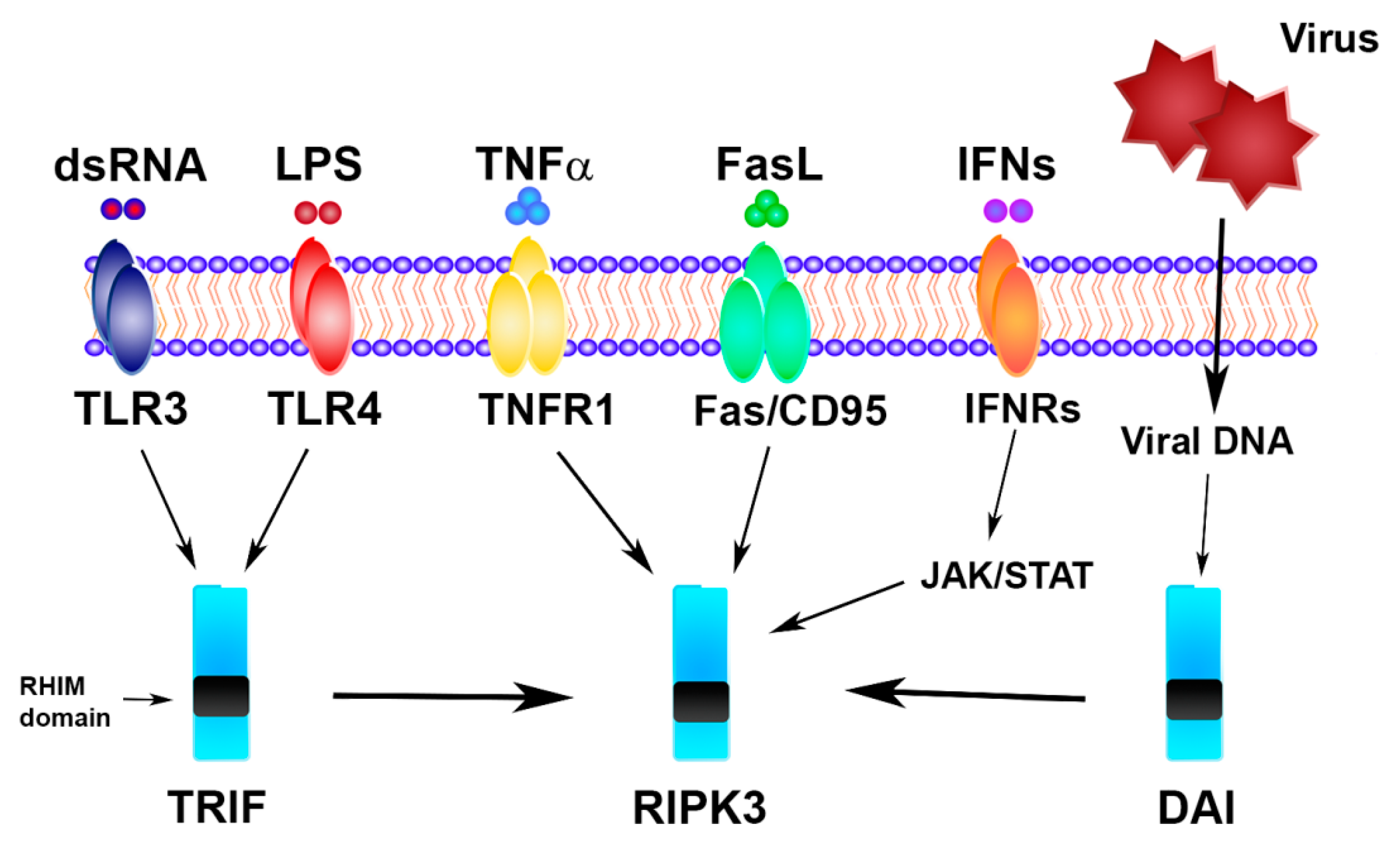
Biomolecules | Free Full-Text | Necroptosis in Intestinal Inflammation and Cancer: New Concepts and Therapeutic Perspectives

LPS-induced expression and release of monocyte tissue factor in patients with haemophilia | SpringerLink

Molecules | Free Full-Text | Anthocyanin-Rich Sour Cherry Extract Attenuates the Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Endothelial Inflammatory Response
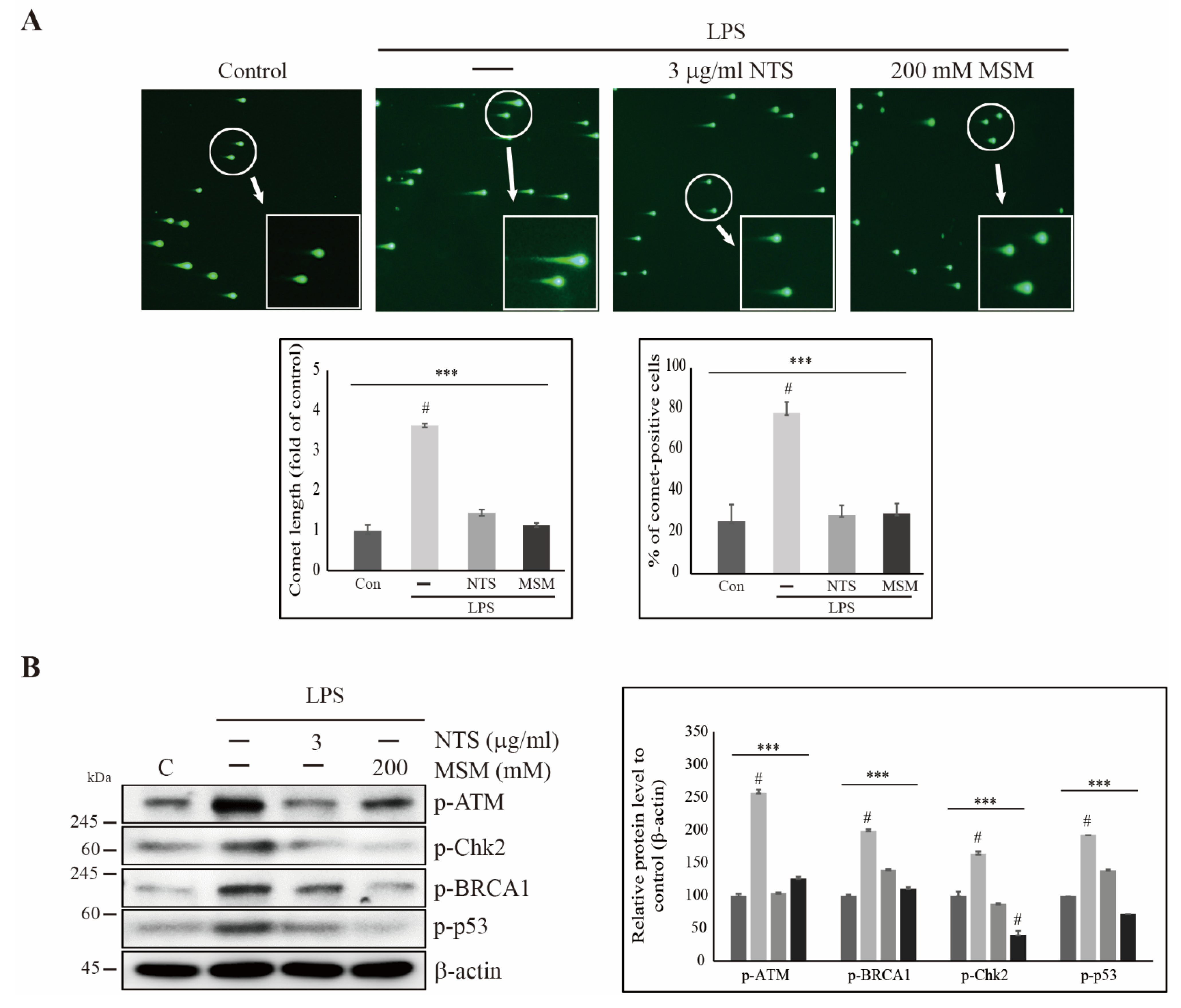
Life | Free Full-Text | Natural Sulfurs Inhibit LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses through NF-κB Signaling in CCD-986Sk Skin Fibroblasts
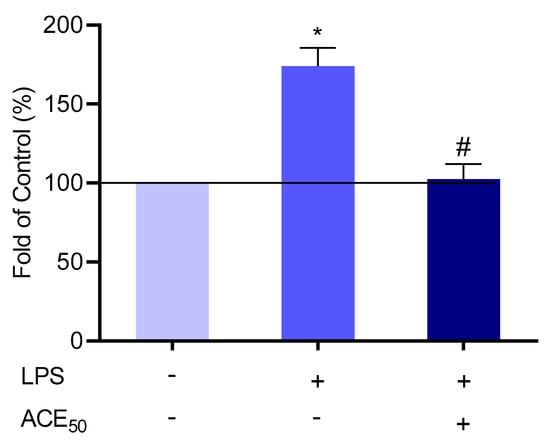
Molecules | Free Full-Text | Anthocyanin-Rich Sour Cherry Extract Attenuates the Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Endothelial Inflammatory Response