Protocol for the Generation of Definitive Hematopoietic Progenitors from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells - ScienceDirect
A novel efficient feeder-free culture system for the derivation of human induced pluripotent stem cells | Scientific Reports
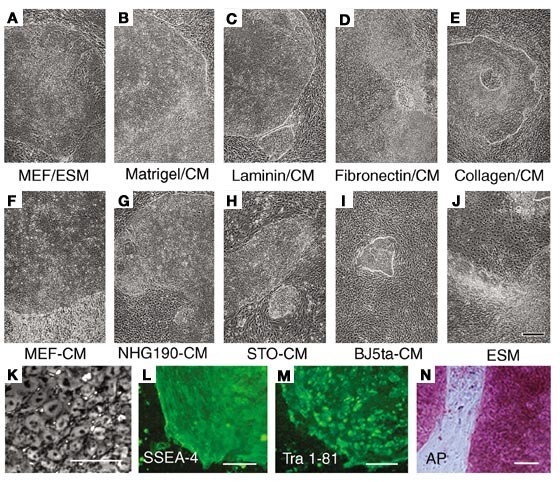
PDF) The Generation of Embryoid Bodies from Feeder-Based or Feeder-Free Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Cultures

Feeder-free generation and transcriptome characterization of functional mesenchymal stromal cells from human pluripotent stem cells - ScienceDirect

Biomedicines | Free Full-Text | A Comparative Study of Cell Culture Conditions during Conversion from Primed to Naive Human Pluripotent Stem Cells
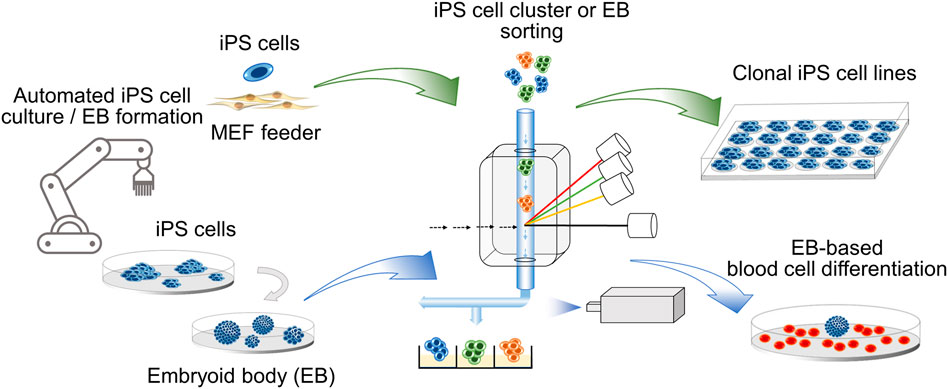
Frontiers | Cell Cluster Sorting in Automated Differentiation of Patient-specific Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Towards Blood Cells

Differentiation of natural killer cells from induced pluripotent stem cells under defined, serum- and feeder-free conditions - Cytotherapy

Direct Comparison of Four Hematopoietic Differentiation Methods from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells - ScienceDirect

A novel efficient feeder-free culture system for the derivation of human induced pluripotent stem cells | Scientific Reports

Morphology of hIDPSCs-iPSCs growing on feeder (A-D) and feeder-free... | Download Scientific Diagram
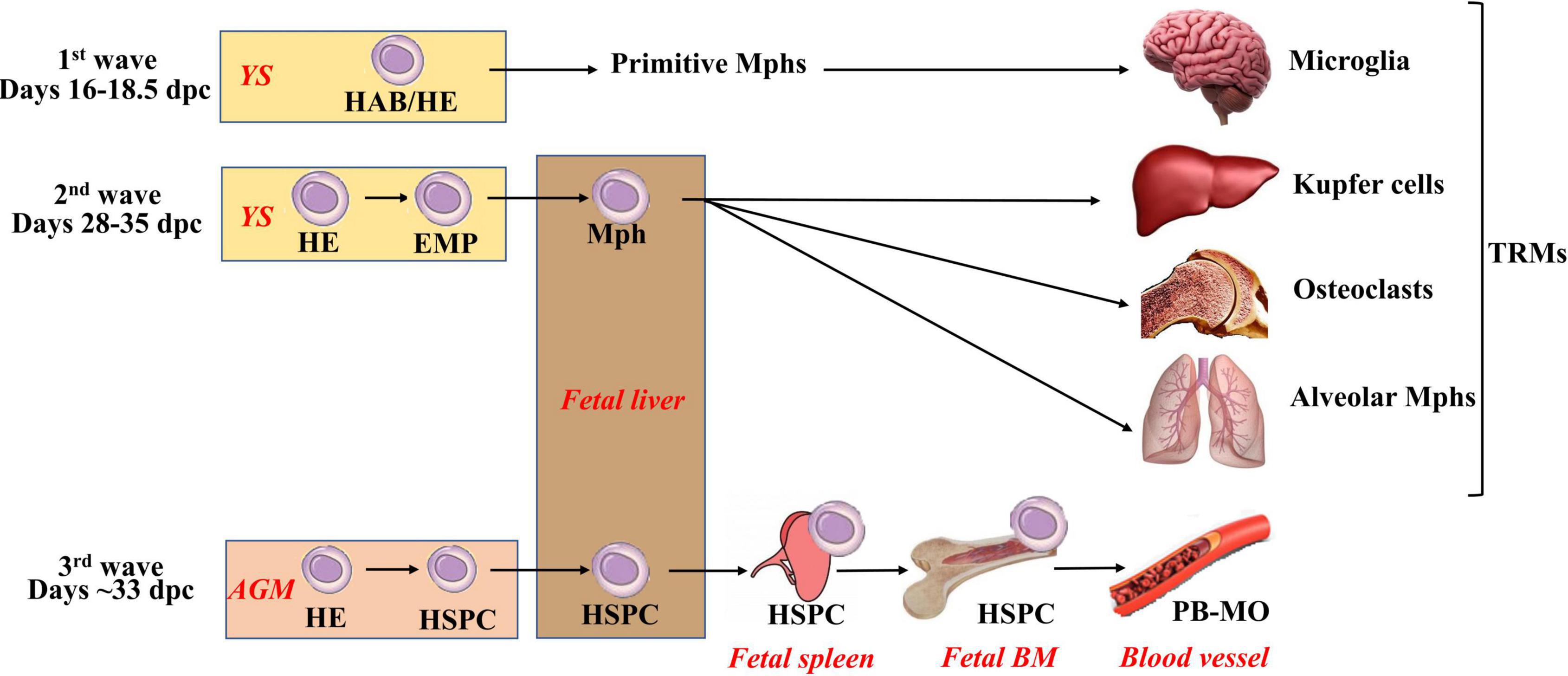
Frontiers | Macrophages Derived From Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells: The Diversity of Protocols, Future Prospects, and Outstanding Questions

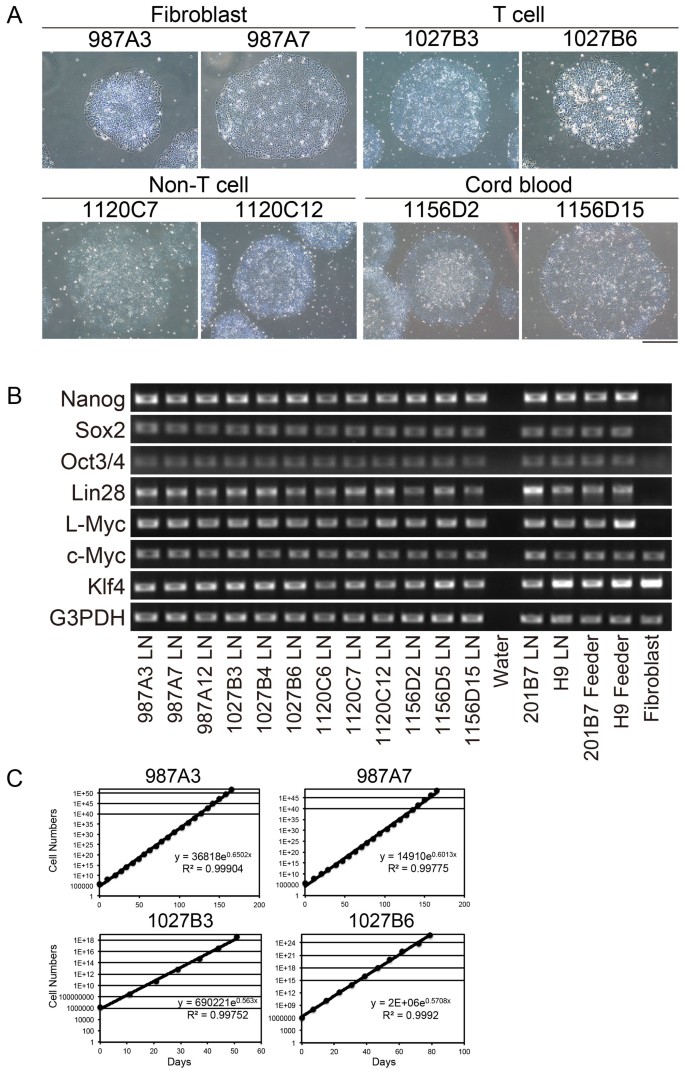
Frontiers | Rapid and Reproducible Differentiation of Hematopoietic and T Cell Progenitors From Pluripotent Stem Cells
Feeder-Free Generation and Long-Term Culture of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Using Pericellular Matrix of Decidua Derived Mesenchymal Cells | PLOS ONE
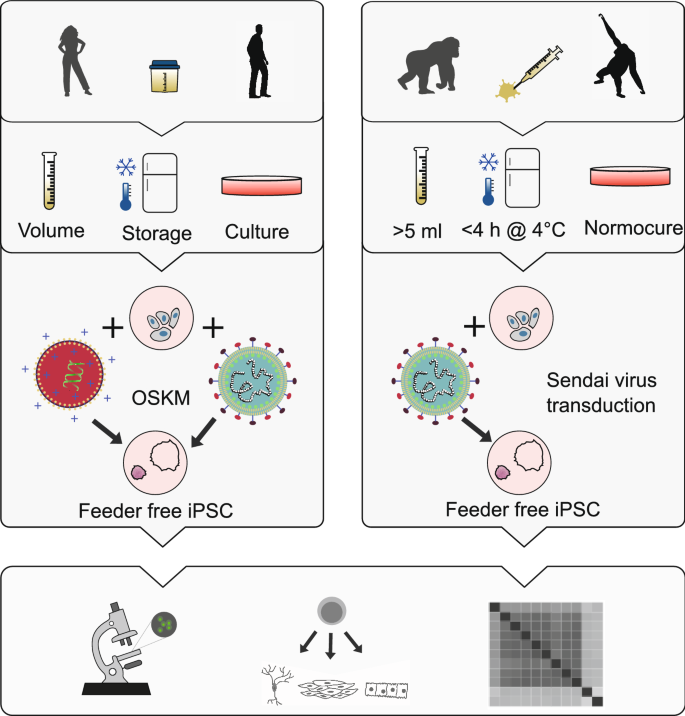
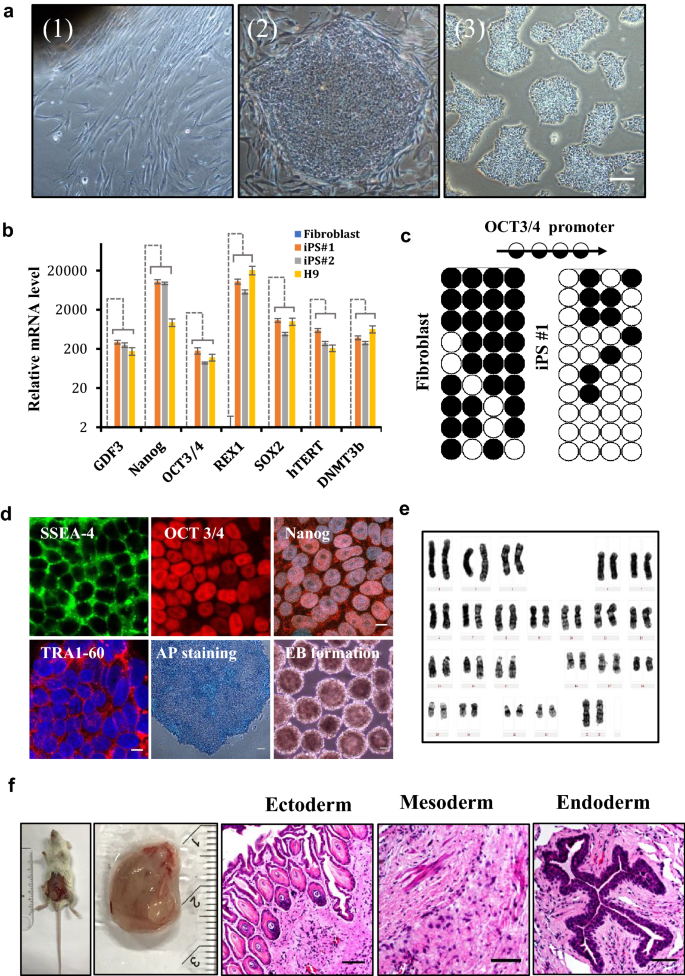
A non-invasive method to generate induced pluripotent stem cells from primate urine | Scientific Reports
Feeder-Free Generation and Long-Term Culture of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Using Pericellular Matrix of Decidua Derived Mesenchymal Cells | PLOS ONE
A Newly Defined and Xeno-Free Culture Medium Supports Every-Other-Day Medium Replacement in the Generation and Long-Term Cultivation of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells | PLOS ONE
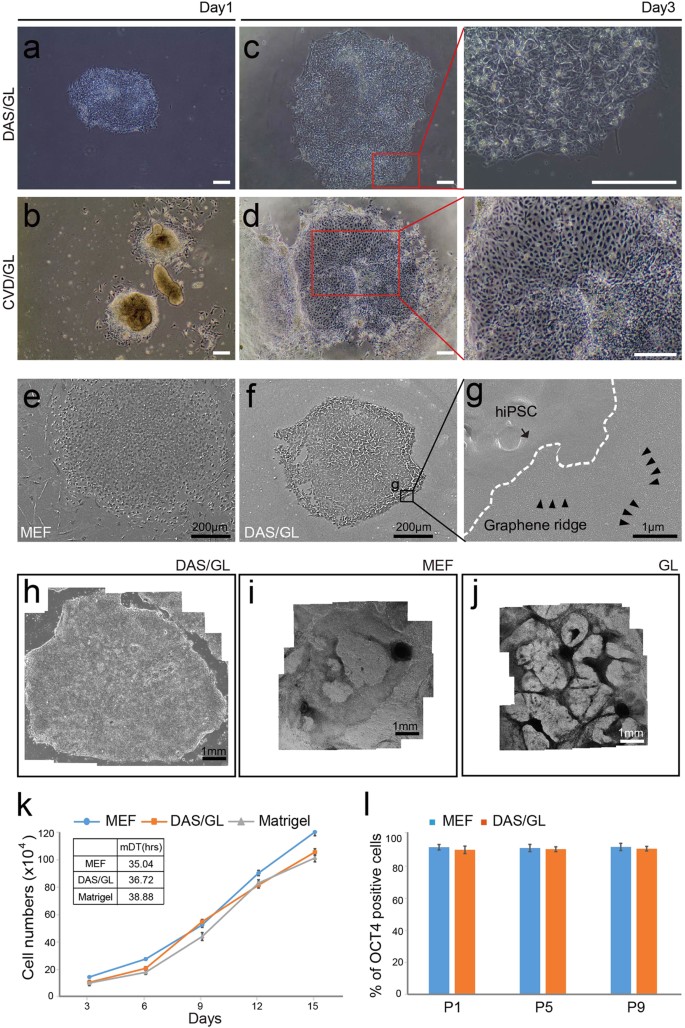
Establishment of feeder-free culture system for human induced pluripotent stem cell on DAS nanocrystalline graphene | Scientific Reports