Role of NAPDH oxidase in Sap-induced netosis. Neutrophils (2.2 × 10 5... | Download Scientific Diagram

PDF) Genetic Variability of Candida albicans Sap8 Propeptide in Isolates from Different Types of Infection
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Plant-Derived Substances in the Fight Against Infections Caused by Candida Species

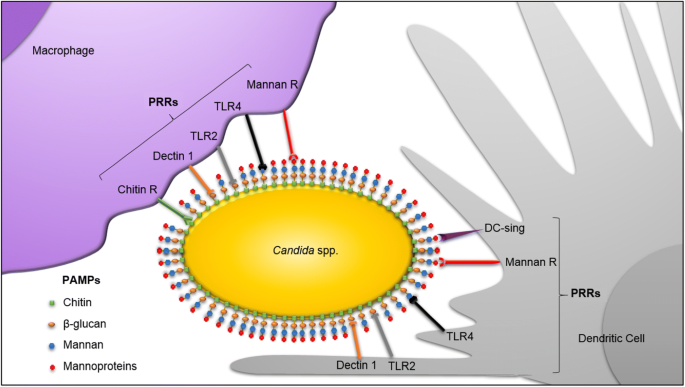
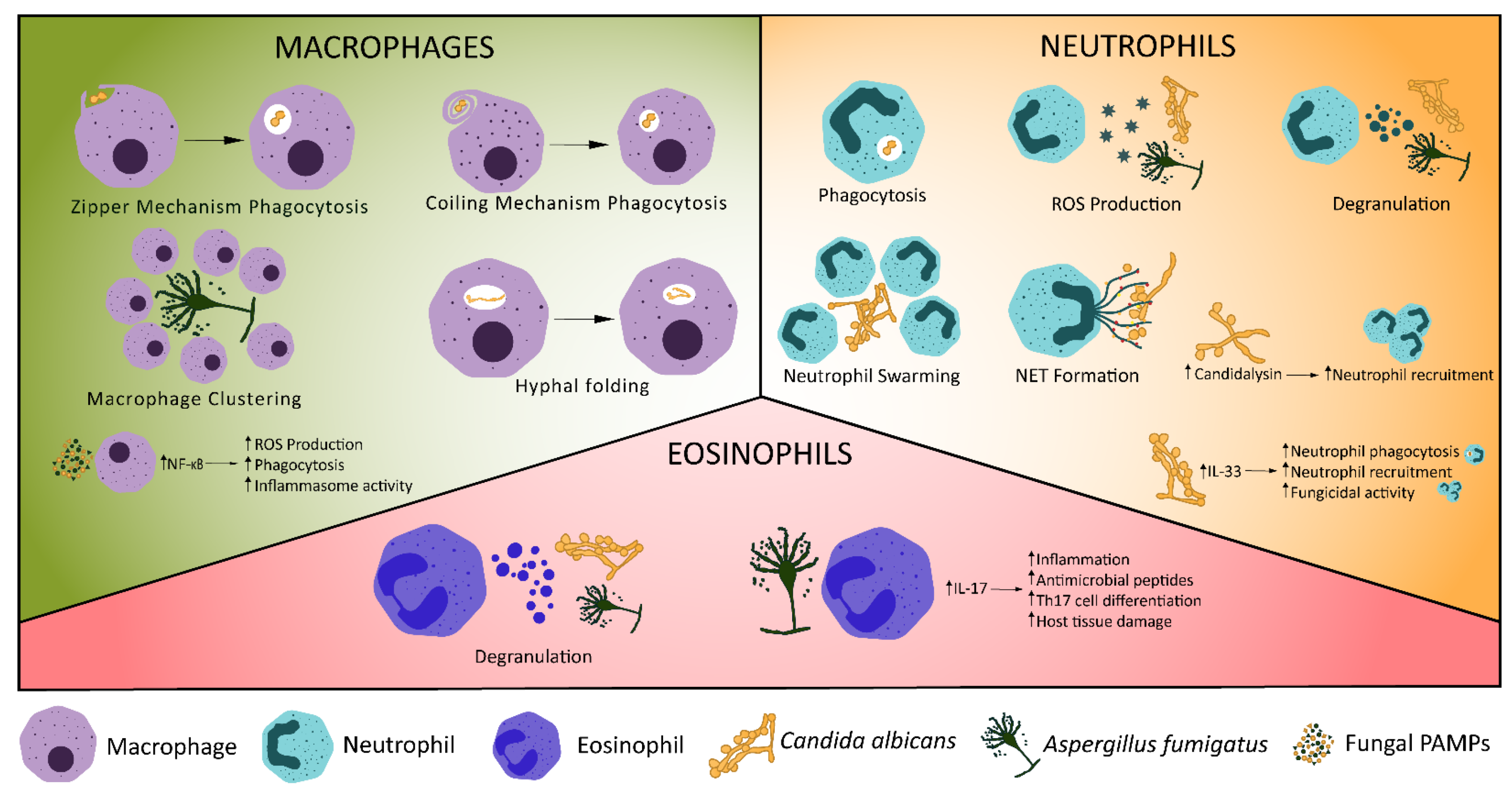
Frontiers | New Insights in Candida albicans Innate Immunity at the Mucosa: Toxins, Epithelium, Metabolism, and Beyond
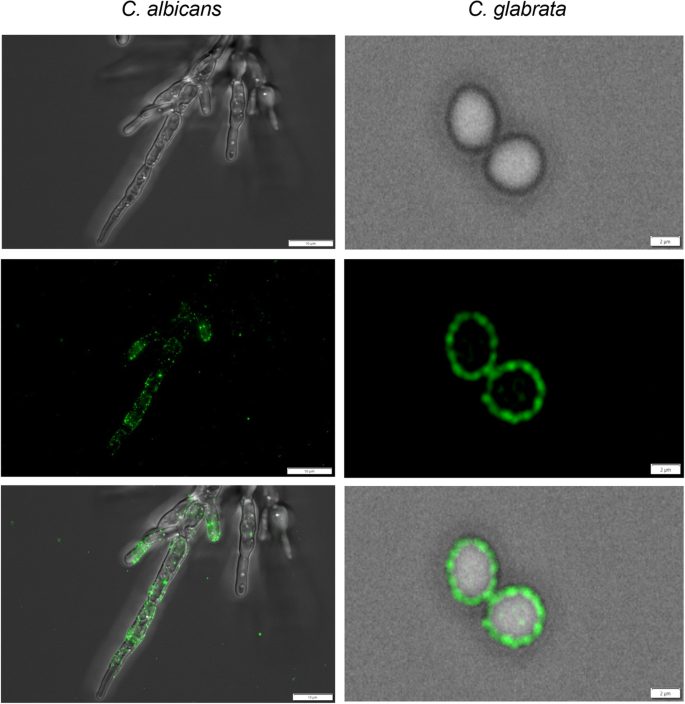
Candida albicans and Candida glabrata triosephosphate isomerase – a moonlighting protein that can be exposed on the candidal cell surface and bind to human extracellular matrix proteins | BMC Microbiology | Full Text

Antifungal activity of SAP-treated LL-37 samples. C. albicans cells... | Download Scientific Diagram

Surface adherence and vacuolar internalization of bacterial pathogens to the Candida spp. cells: Mechanism of persistence and propagation - ScienceDirect
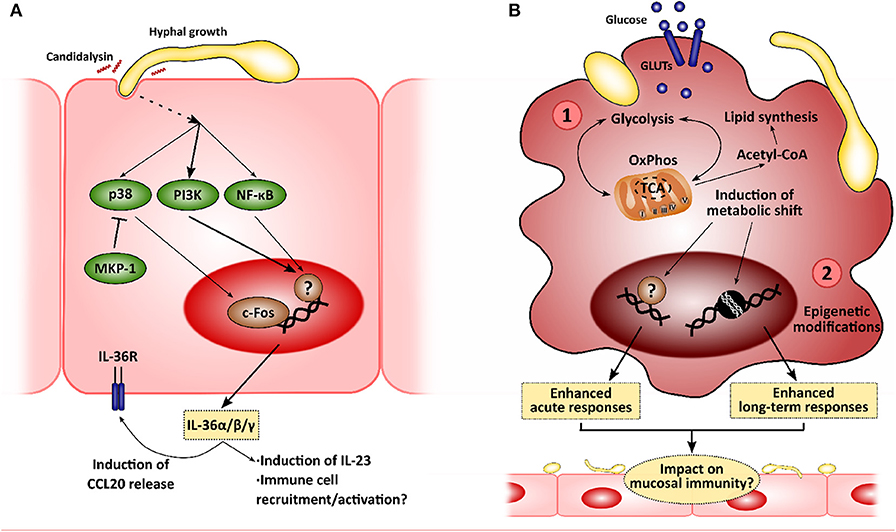
Frontiers | New Insights in Candida albicans Innate Immunity at the Mucosa: Toxins, Epithelium, Metabolism, and Beyond

Proteomics Unravels Extracellular Vesicles as Carriers of Classical Cytoplasmic Proteins in Candida albicans | Journal of Proteome Research

Global Secretome Characterization of the Pathogenic Yeast Candida glabrata | Journal of Proteome Research
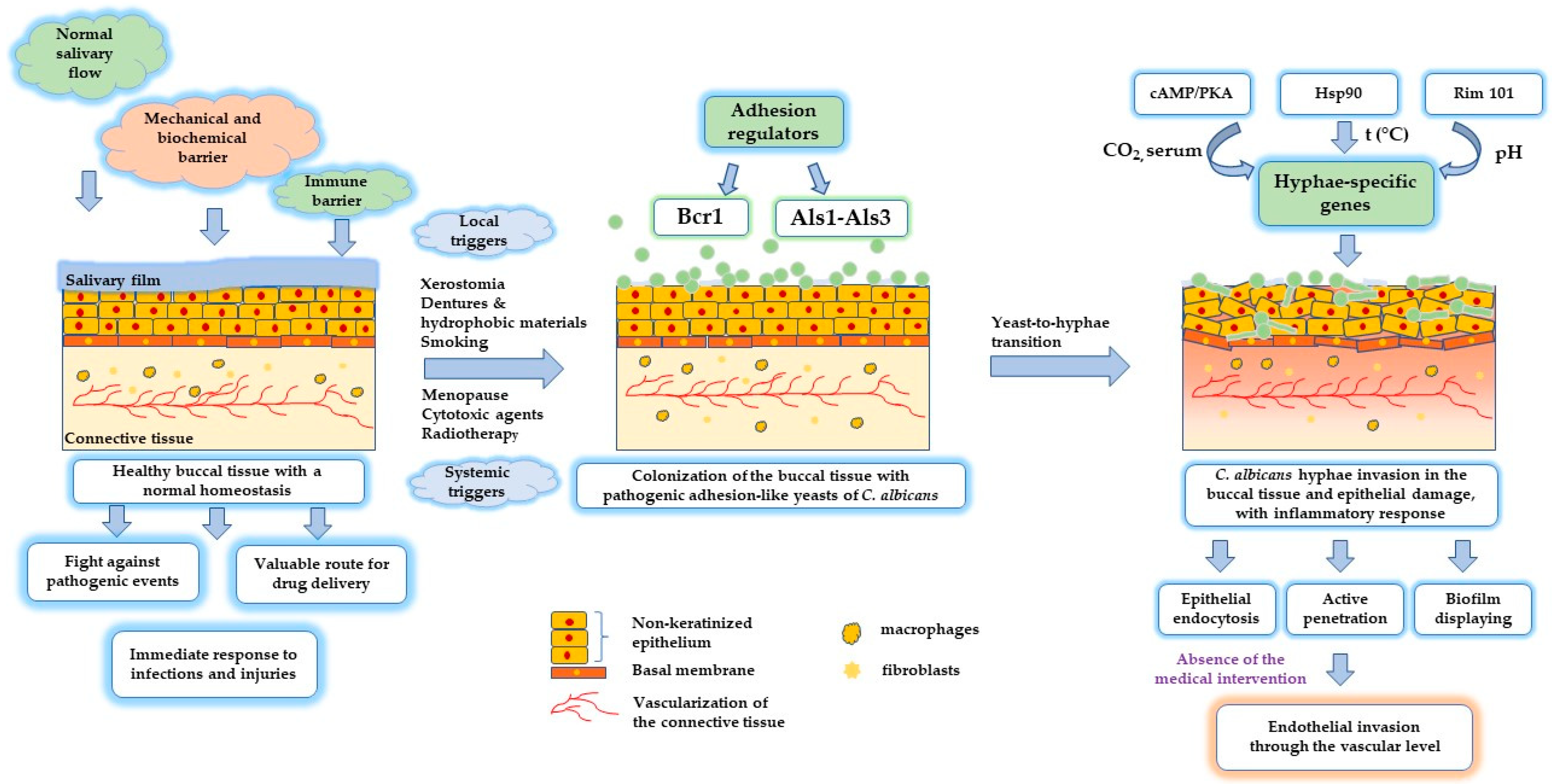
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Molecular Mapping of Antifungal Mechanisms Accessing Biomaterials and New Agents to Target Oral Candidiasis

Inactivation of LL-37 during the interplay between C. albicans cells... | Download Scientific Diagram
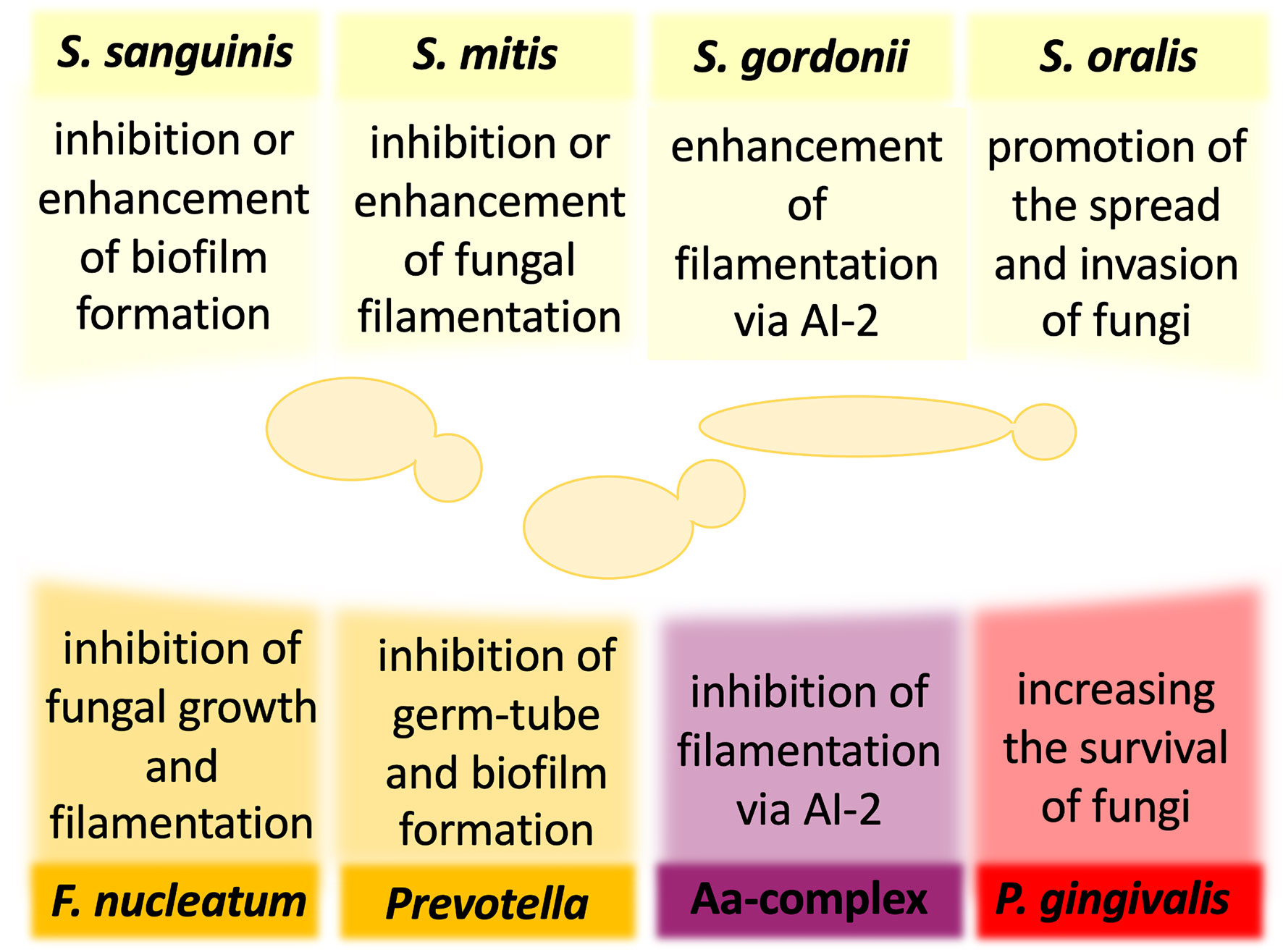
Frontiers | The Role of Candida albicans Virulence Factors in the Formation of Multispecies Biofilms With Bacterial Periodontal Pathogens
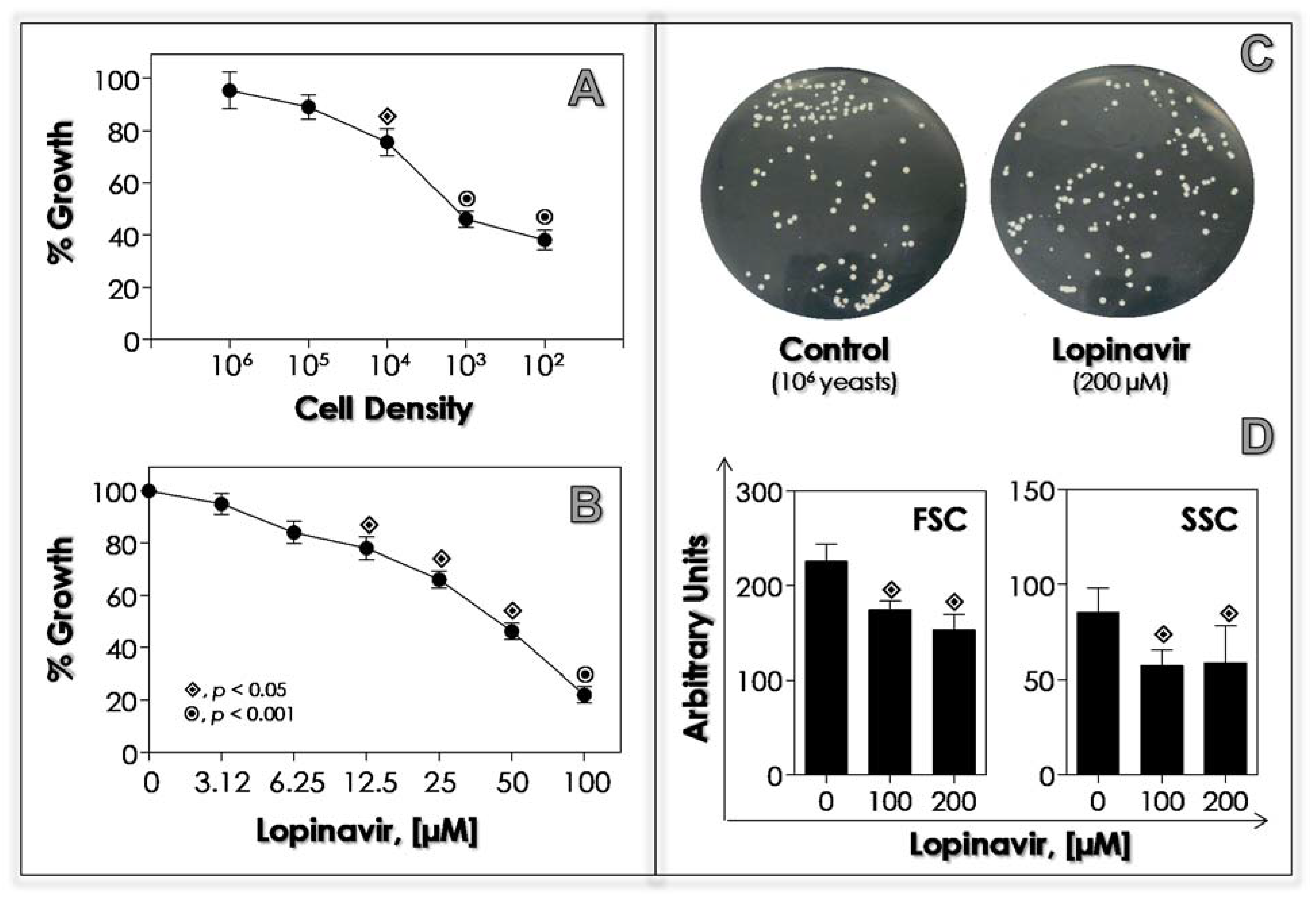
JoF | Free Full-Text | Repositioning Lopinavir, an HIV Protease Inhibitor, as a Promising Antifungal Drug: Lessons Learned from Candida albicans—In Silico, In Vitro and In Vivo Approaches
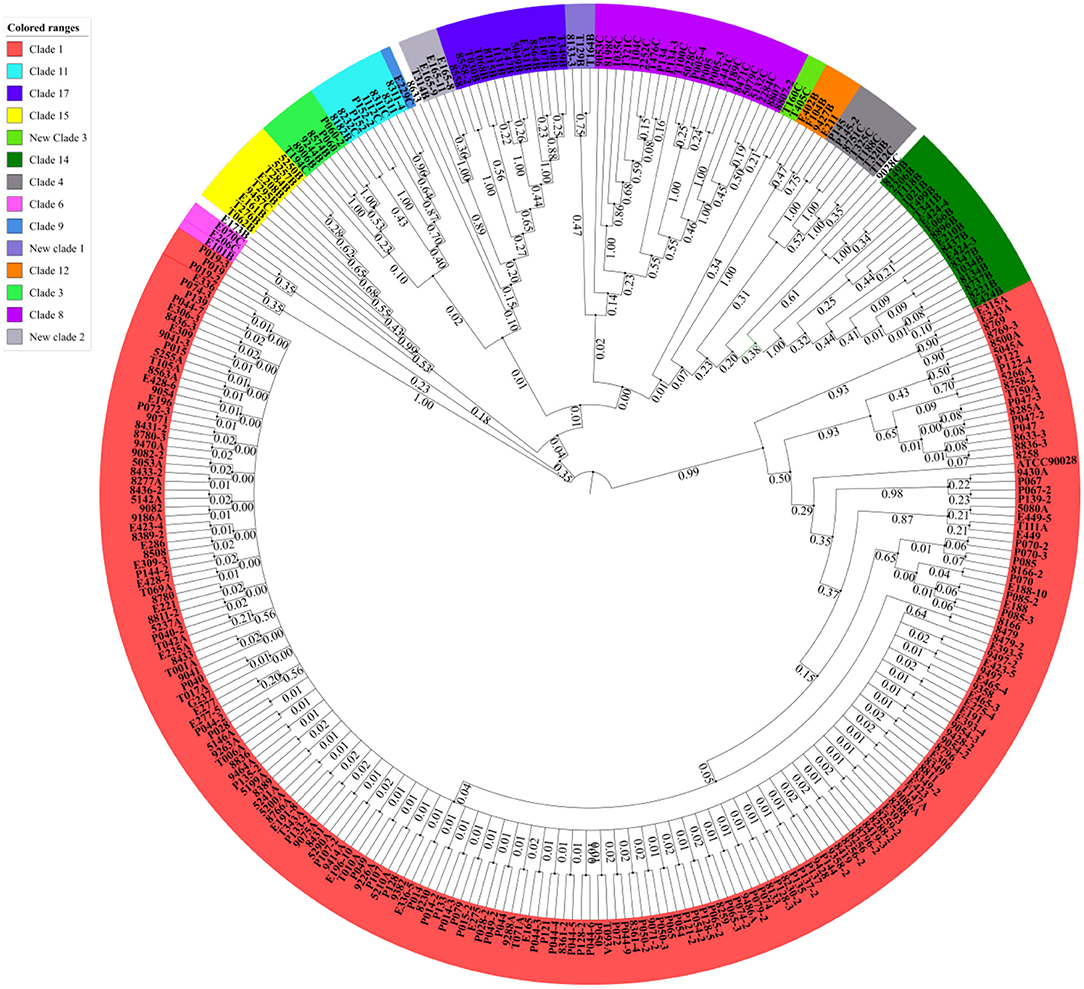
Frontiers | Candida albicans Multilocus Sequence Typing Clade I Contributes to the Clinical Phenotype of Vulvovaginal Candidiasis Patients

Adhesive protein-mediated cross-talk between Candida albicans and Porphyromonas gingivalis in dual species biofilm protects the anaerobic bacterium in unfavorable oxic environment | Scientific Reports

PDF) Kinin release from human kininogen by 10 aspartic proteases produced by pathogenic yeast Candida albicans
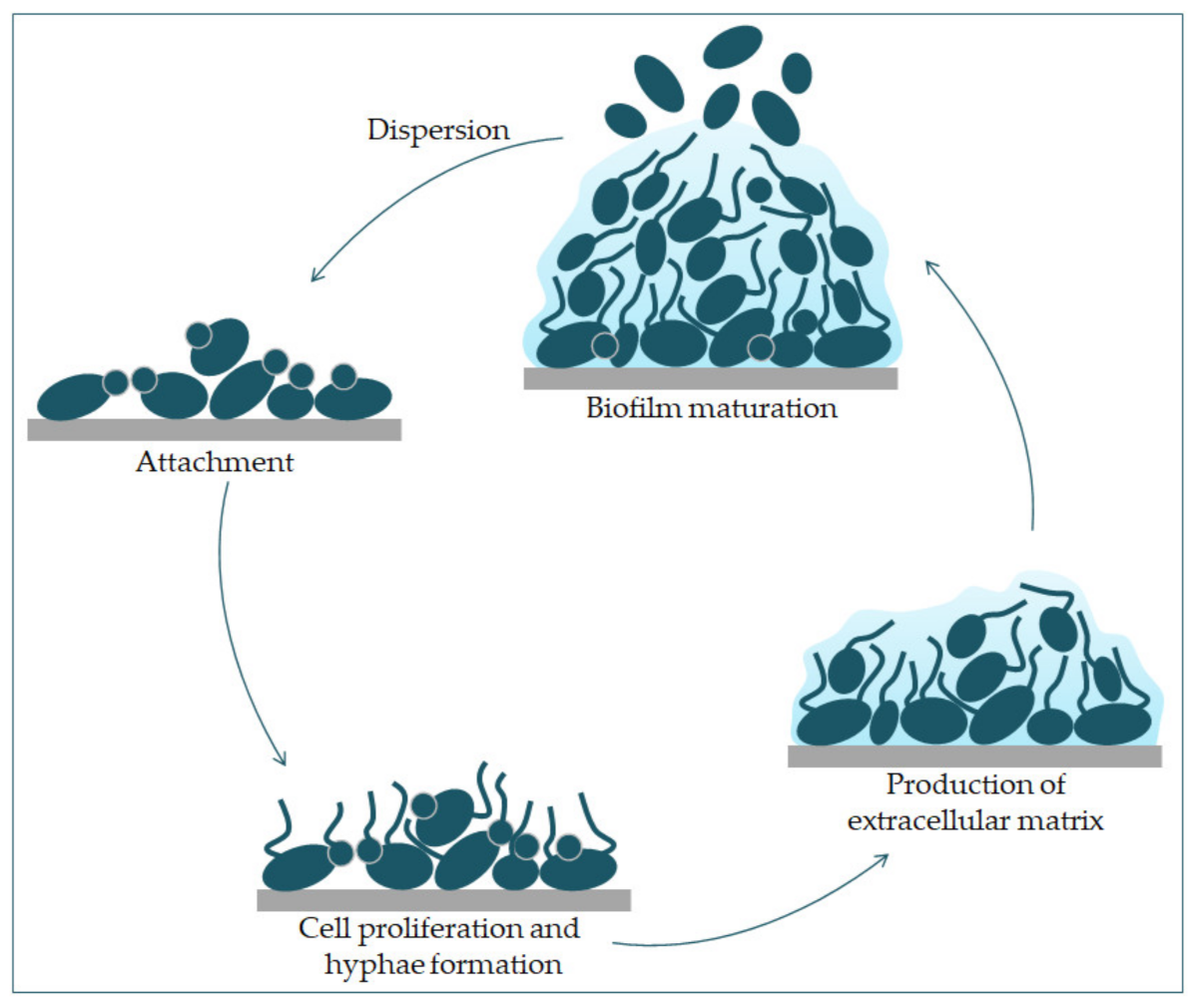
JoF | Free Full-Text | Candida albicans—The Virulence Factors and Clinical Manifestations of Infection

Full article: “Candida Albicans Interactions With The Host: Crossing The Intestinal Epithelial Barrier”
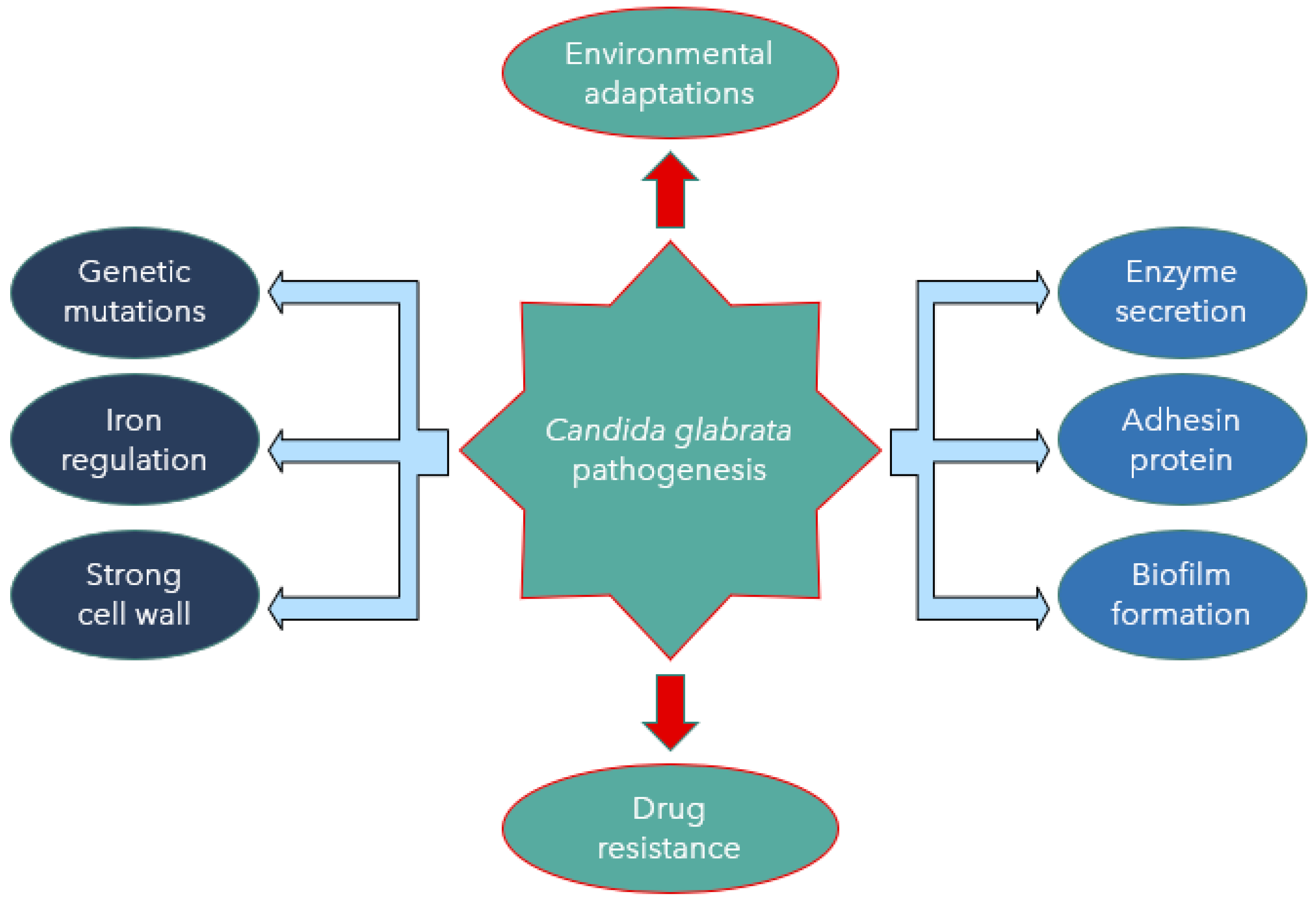
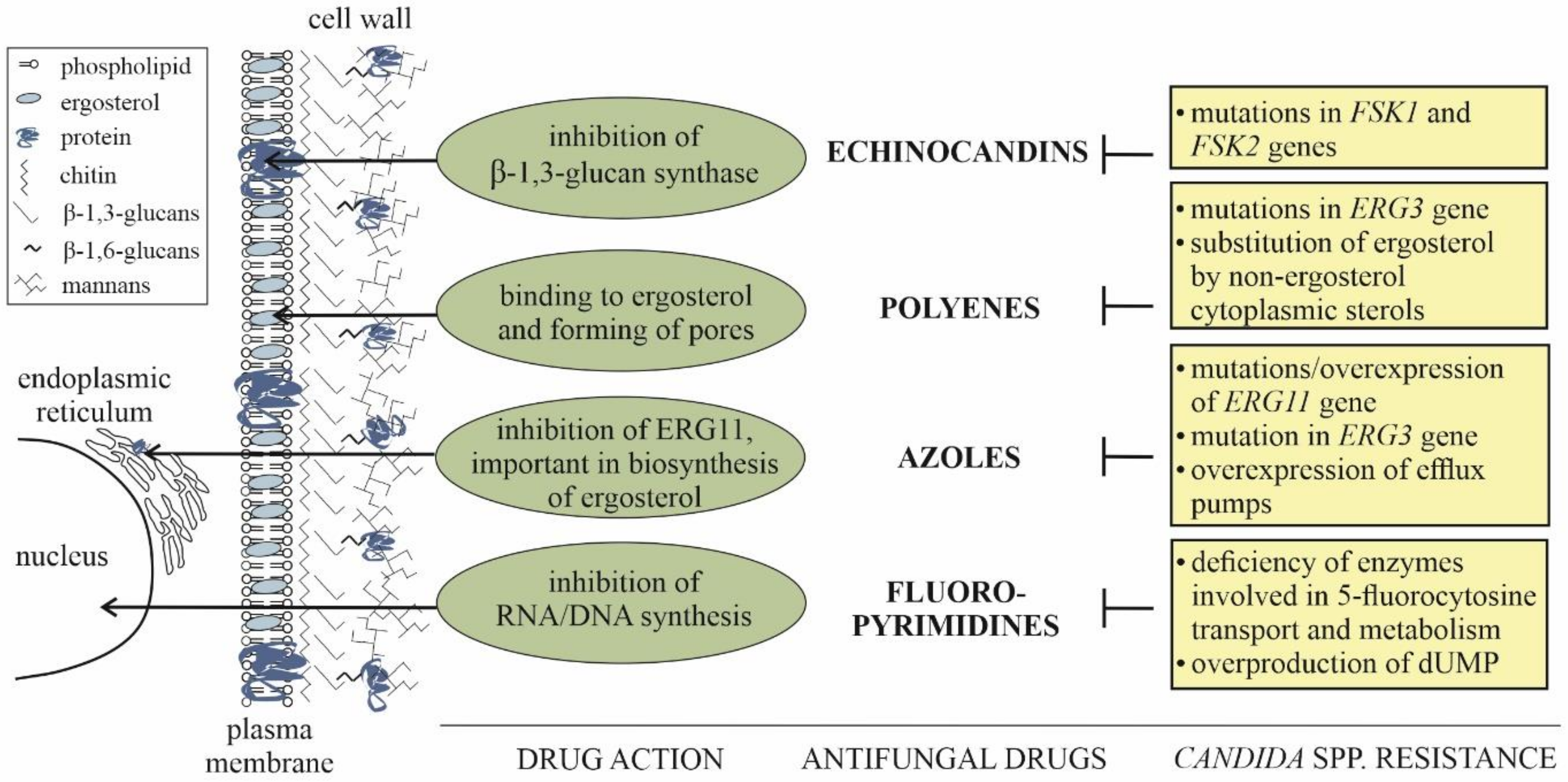
JoF | Free Full-Text | Candida glabrata: Pathogenicity and Resistance Mechanisms for Adaptation and Survival